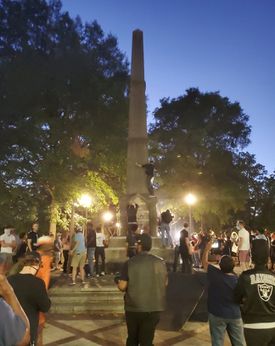Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument.jpg|right|thumb| | [[Image:Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument.jpg|right|thumb|375px|The Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument in 2010]] | ||
The '''Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument''' was a 52-foot-tall sandstone obelisk located at the southern entrance of [[Linn Park]], at the terminus of [[20th Street North]]. It was given to the city by the United Daughters of the Confederacy in [[1905]] and dismantled in [[2020]]. | The '''Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument''' was a 52-foot-tall sandstone obelisk located at the southern entrance of [[Linn Park]], at the terminus of [[20th Street North]]. It was given to the city by the United Daughters of the Confederacy in [[1905]] and dismantled in [[2020]]. | ||
Revision as of 14:07, 5 June 2020
The Confederate Soldiers & Sailors Monument was a 52-foot-tall sandstone obelisk located at the southern entrance of Linn Park, at the terminus of 20th Street North. It was given to the city by the United Daughters of the Confederacy in 1905 and dismantled in 2020.
In 1894 the park, then known as Capitol Park, held no other monuments and was decorated only by towering Hudgins' fountain at its center. The cornerstone for the base for a future monument was laid during the 1894 Reunion of United Confederate Veterans in Birmingham, on April 26, a date observed as Confederate Decoration Day, the anniversary of General Joseph Johnston's surrender to Union General William Sherman at Bennett Place, North Carolina in 1865. It was designed by architect Charles Wheelock and constructed by Joseph Meighan of Oak Hill Marble and Stone Works. The $1,020 cost was raised in four days by a campaign publicized in the Birmingham News. The cornerstone includes a sealed box containing a Bible, a Confederate flag, a bronze medal honoring the Declaration of Independence, several newspapers and lists of Confederate organizations. News publisher Rufus Rhodes introduced UCV Commander-in-Chief Stephen D. Lee, the featured speaker at the ceremony.
Over the next few years, the plinth remained empty. After the Spanish-American War concluded in August 1898 the city installed a surplus artillery piece from the conflict on top of it. In 1900, at the behest of Jennie Rountree, Birmingham's John Pelham Chapter of the United Daughters of the Confederacy, organized in 1896, took up the challenge of completing the Confederate monument. Mrs A. A. Clisby, president of the chapter, appointed Mary Scott Taliaferro, Mrs J. U. Hardeman, Mrs R. H. Carter, and Mrs Charles G. Brown to a committee to raise funds. The committee organized a week-long bazaar in the City Market on the ground floor of Birmingham City Hall. Clisby's successors carried the torch and made annual appeals for funds through the Birmingham News.
In October 1904 Camp W. J. Hardee, United Confederate Veterans voted to contribute $500 toward the efforts of the Daughters and Sons of the Confederacy, raising the overall fund to $1,700. Some commenters were, "not so sure but that the expenditure of only $1,700 will not be more of a humiliation than an honor," compared to the grandeur of the large monument on the grounds of the Alabama state capitol, erected at a cost of more than $30,000. In the event, more contributions did arrive, and once $4,000 was raised, the Pelham Chapter, now with Mrs Rountree as its president, commissioned stone contractor L. N. Archer to fabricate and install the obelisk.
The completed monument was formally dedicated on April 26, 1905, now observed for the first time, statewide as "Confederate Memorial Day". A grand parade of over 1,000 people, including the entire student body of Birmingham High School, the corps of cadets from Howard College, the Birmingham Police Department and Birmingham Fire Department, numerous "carriages and tally-hos," and several military bands, made its way from Jefferson County Courthouse to the park. Jennie Rountree introduced her committee chair, Mrs Brown, by saying, "The strength of that shaft, fifty-two feet high, stands as evidence of the united strength of Pelham Chapter, the members of which have stood shoulder to shoulder, side by side, caring ever for the needs of the less fortunate who fought for Southern rights, honoring with our cross of bronze the Confederate soldier wherever found, and strewing flowers over the graves of those who have gone beyond. You have met with us here today to witness the completion of our work in commemoration of the deeds of valor to the entire Confederacy, and on behalf of our chapter, I present to you the chairman of our monument committee, Mrs Charles G. Brown."
Brown then presented the monument to the State of Alabama and to the City of Birmingham. Lieutenant Governor Russell Cunningham and Mayor Mel Drennen then graciously accepted the gift with speeches of their own. General George P. Harrison, Commander of the United Confederate Veterans of Alabama, gave the concluding address to rounds of raucous applause punctuated by the "rebel yell" from fellow veterans. After the conclusion of the ceremony, the crowd processed up to Oak Hill Cemetery to decorate the graves of 45 Confederate dead.
Inscriptions
- (south face)
TO THE CONFEDERATE SOLDIER & SAILOR
ERECTED BY PELHAM CHAPTER No. 67
DAUGHTERS OF THE CONFEDERACY
BIRMINGHAM, ALA.
APRIL 26, 1905
- (north face)
"THE MANNER OF THEIR
DEATH, WAS THE CROWNING
GLORY OF THEIR LIVES."
JEFFERSON DAVIS.
- (west face)
A relief sculpture of an anchor to represent the Confederate Navy
- (east face)
A relief sculpture of crossed sabers and a musket to represent the Confederate Cavalry and Infantry
Relocation proposals
The possibility of removing the monument was implicit in the 1919 proposal by architects Frank Hartley Anderson, William Warren and Eugene Knight for a Memorial Civic Center that would serve as a comprehensive memorial with an emphasis on the recently-ended "Great War". During his visit for the Olmsted Brothers' 1925 report and recommendations for "A Park System for Birmingham" landscape architect W. B. Marquis wrote that "The Confederate Monument located on the axis of 20th St. at the south end of the park probably must be retained although there may be some possibility of changing its position." The firm, delayed by uncertainties about the designs for a new Birmingham Public Library and Jefferson County Courthouse, never presented a detailed plan for redesigning what was, by then, renamed Woodrow Wilson Park. In their report they merely recommended that the park "is generally considered as a possible civic center and should, if possible, be so planned and developed."
In 2015, in the wake of a mass shooting at an African Methodist Episcopal church in Charleston, South Carolina, activist Frank Matthews and others called for the monument to be removed on the grounds that its depiction of deadly weapons alongside quotes from Jefferson Davis were offensive, and that its sentiment has nothing to do with Birmingham. The Birmingham Park and Recreation Board voted on July 1 to pursue relocating the monument by consulting with attorneys and with the United Daughters of the Confederacy.
A group called "Save our South" filed a lawsuit against the Park Board and City Council seeking a restraining order to prevent the board from removing the memorial. Judge Mike Graffeo dismissed the suit in November.
During the Alabama State Legislature's 2016 session, State Senator Gerald Allen of Tuscaloosa introduced a bill he called the "Alabama Heritage Protection Act" which would "prohibit the relocation, removal, alteration, renaming, or other disturbance of certain commemorative statues, monuments, memorials, or plaques which are located on public property," without being granted an express waiver from the state legislature. The act, which would also prevent the renaming of public buildings, streets, bridges and parks, made an exception for any such removals undertaken for transportation projects. The bill passed the Senate and a House committee, but did not come to a vote in the House during that session. It was brought back in 2017 and passed both houses of the legislature. It was signed into law by Governor Kay Ivey on May 24 as the "Alabama Memorial Preservation Act".
On August 15, 2017, in the wake of a violent rally of white nationalists gathered to oppose the removal of a statue of Robert E. Lee in Charlottesville, Virginia, Mayor Bell ordered that the monument should be covered and walled off until a legal means of removing it could be established. Alabama Attorney General Steve Marshall then filed suit against the city, claiming that the action violated the recently-passed law. A hearing in that case was held on April 13 before Jefferson County Circuit Court Judge Mike Graffeo. Graffeo issued a ruling shortly before his January 2019 retirement from the bench voiding the 2017 law on the basis that it attempted to restrict the right of the citizens of Birmingham to speak collectively through their city government, and that it deprived the city of the right of due process. Activist Frank Matthews responded to the ruling by calling for the Birmingham Board of Parks and Recreation to remove the monument immediately.
Marshall appealed Graffeo's ruling to the Alabama Supreme Court, which reversed Graffeo, instructing him to order the city to remove the barricade and pay a $25,000 fine. The court stated that the barricade negated the monument's intent, saying that, "Members of the public passing through Linn Park could have no way of knowing what the marble shaft rising from behind the plywood screen was intended to memorialize," and further ruled that municipalities do not enjoy the rights guaranteed by the constitution to individuals. The city filed a petition for a re-hearing, but it was denied.
Vandalism and removal
The statue was significantly damaged and defaced with hand tools, power tools, and spray paint during riots on the night of May 31, 2020, coinciding with national protests in response to the death of George Floyd at the hands of police in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Attempts to topple the obelisk were unsuccessful. Mayor Randall Woodfin told the crowd that he would finish the job they started within 24 hours. Other monuments in the park were also damaged before police cleared the park shortly after 10:00 PM. The city enforced a curfew the following night.
The next day, Monday June 1, coincidentally a state holiday honoring Jefferson Davis, Marshall issued a statement affirming that he would file suit under the state law in pursuit of a fine, which he clarified was, "a one-time assessment of $25,000." That evening, during a citywide emergency curfew, the monument was removed from the park. Woodfin said that the cost to the city for the work of removing it was $1, but did not identify the contractor due to fears of backlash. A GoFundMe campaign was launched by White Clergy for Black Lives Matter to reimburse any costs and potential state penalties for removing the monument. The campaign received more than $60,000 in less than 24 hours. Organizers pledged to forward donations above that amount to Faith in Action Alabama to help eliminate systemic racism in the state. A seprate GoFundMe campaign was launched by the Penny Foundation later that night to address the same costs as well as, "the erection of a new monument."
The city does not intend to destroy the historical monument, and is storing it at an undisclosed location until a determination is made about where it should go. The Mayor's office has made attempts to contact the Sons of Confederate Veterans and the United Daughters of the Confederacy, as well as other organizations, about taking possession of the monument, but no agreement has been reached. Any artifacts recovered from the monument will also be preserved.
References
- "Daughters and Sons of the Confederacy and the United Confederate Veterans to Build Monument." (November 10, 1904) Jones Valley Times, p. 1
- "Confederate Monument is Unveiled in Capitol Park." (April 27, 1905) Birmingham Age-Herald, p. 5
- "The Birmingham Confederate Monument" (August 1908) Confederate Veteran. Vol. 16, No. 8
- Sulzby, James F. Jr (1945) Birmingham Sketches From 1871 Through 1921. Birmingham: Birmingham Printing Company, pp. 133-136
- Davis, Michael: "In Remembrance: Confederate Funerary Monuments in Alabama and Resistance to Reconciliation, 1884-1923" May 10, 2008 - accessed October 20, 2010
- Wright, Barnett (June 23, 2015) "Activist Frank Matthews: Remove the 'racist' Confederate monument from Birmingham." The Birmingham News
- Bryant, Joseph D. (July 1, 2015) "Birmingham city officials take steps to remove Confederate monument at Linn Park." The Birmingham News
- Almond, Mark (July 2, 2015) "A close-up look at Birmingham's embattled Confederate monument." The Birmingham News
- Birmingham Historical Society Newsletter (July 2015)
- Stein, Kelsey (August 19, 2015) "Decision about fate of Birmingham Confederate monument should not be rushed, attorneys say." The Birmingham News
- Edgemon, Erin (August 15, 2017) "Birmingham covers Confederate monument as city considers removal." The Birmingham News
- Edgemon, Erin (August 16, 2017) "AG files lawsuit against Birmingham over Confederate monument." The Birmingham News
- Hrynkiw, Ivana (April 13, 2018) "AG, Birmingham attorneys argue over Confederate memorial." The Birmingham News
- Crenshaw, Solomon Jr (April 13, 2018) "Questions Raised About Legal Protections for Historic Monuments in Court Hearing Over Linn Park’s Plywood Screen" BirminghamWatch
- Hrynkiw, Ivana (January 15, 2019) "Judge rules Alabama Confederate monument law is void; city of Birmingham didn’t break the law." The Birmingham News
- Hrynkiw, Ivana (January 16, 2019) "Birmingham activist calls for removal of Linn Park monument." The Birmingham News
- Prickett, Sam (November 27, 2019) "High Court Rules Confederate Monument Outside Birmingham City Hall Cannot Be Covered, Fines City" BirminghamWatch
- Whitmire, Kyle (December 4, 2019) "This is our history: How white supremacy still thrives in Alabama." The Birmingham News
- Whitmire, Kyle (June 1, 2020) "When a Confederate monument wouldn’t fall, rioters turned on Birmingham." The Birmingham News
- "Attorney General Steve Marshall Statement on Birmingham Linn Park Confederate Monument." (June 1, 2020) press release
- Sheets, Connor (June 2, 2020) "Obituary for a racist symbol: Birmingham takes down Confederate monument after 115 years." The Birmingham News
- Koplowitz, Howard & Jeremy Gray (June 2, 2020) "Where did Birmingham’s Confederate monument go? Mayor won’t say." The Birmingham News
- Koplowitz, Howard (June 2, 2020) "Alabama attorney general sues Birmingham for removing Confederate monument." The Birmingham News
- Dunigan, Jonece Starr (June 3, 2020) "Confederate cornerstone removed from Birmingham park." The Birmingham News
- Whitmire, Kyle (June 3, 2020) "Birmingham’s Confederate monument is gone, but what lies beneath is still there." The Birmingham News
External links
- Take Down Birmingham's Confederate Monument on GoFundMe
- Monumental. on GoFundMe